LMD in UMBB
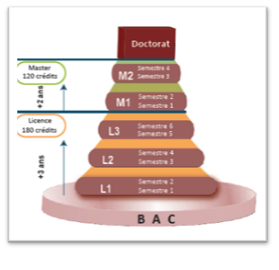
A three-level structure
- The lessons are semester-based:
- • A Bachelor's degree includes 6 semesters of teaching (from S1 to S6)
- • A Master has 4 of them (from S1 to S4).
- • A semester counts as 30 credits.
- • For each teaching unit, the number of ECTS is calculated on the basis of a volume of hours, lessons, personal work.
- • The credits can also validate an internship, according to the procedures provided for in each training course.
- • The student obtains his degree after validation of 180 credits. He obtains his Master after validation of 120 additional credits.
- • These credits are an international recognition, they are:
- Transferable for the student who carries out part of his training in another university establishment, or changes his course during the training,
- Capitalizable, therefore definitively acquired, regardless of the duration of the student's course.
Capitalization
Within a training course, the teaching units are definitively acquired and capitalized as soon as the student has obtained the compensated average between the subjects of the same teaching unit. The acquisition of the teaching unit involves the capitalization of its credits
Compensation :
Each course unit is assigned a credit value and a coefficient. The value in credits being the sum of the credits of its subjects. Compensation is made per unit, between units of the same semester or between units for the year.
Compensation per unit is organized on the basis of its subjects weighted by their coefficients (a subject also has a credit value and a coefficient.
The compensation between units of the same semester is organized on the basis of the averages obtained for the various weighted units by the coefficient speakers.
The compensation between units from the two semesters of the same year is organized on the basis of the averages obtained for the various units weighted by their coefficients.
Progression
- 1. License Progress
- Admission to the next year is as follows:
- From 1st to 2nd year: total a minimum of 30 credits out of the 60 for the year.
- From the 2nd to the 3rd year: total a minimum of 80% of the credits of the first two years of the bachelor's degree with the validation of the Fundamental Teaching Units.
NB: In either case, the opinion of the training team is required if the number of credits is less than 60 (passage from the 1st to the 2nd year) or 120 (passage from the 2nd in 3rd year). If the student is accepted for conditional admission, it will be up to him to make up the missing credits. The training team can set up a special evaluation device to allow the student to be directed to another training course
- 2. Master's progression
-
• Progression from M1 to M2 is for students who have acquired all the credits for S1 and S2 of the 1st Year, i.e. 60 credits. There is no compensation between the 2 semesters.
- A semester of studies is obtained either by acquiring each teaching unit, or by applying compensation between the teaching units of this semester. In either case, the student must total 30 credits to validate the semester. The year is obtained by the acquisition of its two semesters. The student acquires 60 credits if he validates both semesters of the same year.
-
• Practical guide to implementing and monitoring the LMD (June 2011):
Study in the LMD System (Master)
Diplomas prepared :
Master ‘s degree: Bac + 5;
(A): Academic degree, (P): Professional degree.
(*) : offer submitted to the MESRS for authorization.
Masters Fields of Training SM, MI, SNV, STAPS, LLE, LLA, SEGC, DSP, ST ( St, Sthy ; Stel)
Training places: Faculty of Sciences (FS) Fields (SM, MI, SNV, STAPS)
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Science
of Matter
(SM)
| Chemistry |
- Water Chemistry (A)
- Environmental Chemistry (A)
- Materials Chemistry (A)
- Inorganic Chemistry (A)
- Analytical Chemistry (A)
- Organic Chemistry (A)
|
| Physics |
- Fluid Dynamics and Energetics (A)
- Condensed Matter Physics (A)
- Materials Physics (A)
- Radiation Physics (A)
- Energy Physics andRenewable Energies (A)
- Energetic Physics and Renewable Energies: Gas and Transfers (A)
|
| Mathematics and Computing
(MC)
| Computing |
- Software Engineering and Data Processing (A)
- Distributed Information Systems (P)
- Information Technology (P)
|
| Mathematics |
- Mathematical Analysis (A)
|
| Applied Mathematics |
- Financial Mathematics (A)
- Stochastic and Statistical Modeling (A)
- Operational Research: Optimization and Strategic
Management (A)
|
| Natural and Life Sciences
(NLS)
|
Biotechnology |
- Biotechnology and Molecular Pathology (A)
- Microbial Biotechnology (A)
- Plant Biotechnology (A)
|
| Ecology and Environment |
- Agroenvironment and Bio-Indicators (A)
- Biodiversity and Environment (A)
|
| Agronomy Sciences |
- Phytopharmacy and Plant Protection (A)
- Production and Animal Nutrition (A)
- Plant production (A)
- Phytopathology (A)
|
| Food Science |
- Nutrition and Food Sciences (A)
|
| Biological Sciences |
- Applied Biochemistry (A)
- Biology of Populations and Organisms (A)
- Genetics(A)
- Cell Physiology and Physiopathology (A)
|
| Science and
Techniques of
Physical and Sports Activities
(STPSA)
|
Physical Education and Sport Activities |
- School Physical and Sports Activity (A)
|
| Sport Training |
- Elite Sports Training (A)
|
Training places: Faculty Of Technologie (FT) Fields of Training ST (ST, SThy, STelec)
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Science and Technology ST)
| Automatic |
- Automation and Industrial Computing (A)
|
| Electronique |
- Automation (Master with Integrated Bachelor’s Degree Curriculum (MCIL)
|
| Electronic |
- Electronics of Embedded Systems (A)
|
| Electrotechnics |
|
| Mechanical Engineering |
- Mechanical Construction (A)
- Energetics(A)
- Mechanical and Production Manufacturing (A)
- Materials Engineering (A)
- Energy Installations and Turbomachinery (A)
- Boiler work and Piping (P)
- Metal working and Boilermaking (P)
- Maintenance Engineering (P)
- Renewable Energies in Mechanics (A)
|
| Civil Engineering |
- Geotechnics (A)
- Materials in Civil Engineering (A)
- Structures (A)
- Structures and Buildings (P)
|
| Industrial Engineering |
- Industrial Engineering (A)
|
| Process Engineering |
- Food Engineering (A)
- Chemical Engineering (A)
- Polymer Engineering (A)
- Materials Process Engineering (A)
- Environmental Engineering (A)
- Environmental Process Engineering (A)
- Engineering and Water Management (A)
|
| Electromechanics |
- Electromechanics (A)
- Industrial Maintenance (A)
- Mechatronics (A)
|
| Health and Industrial Safety |
- Health and Industrial Safety (A)
|
| Biomedical Engineering |
- Biomedical Instruments (A)
|
| Telecommunications |
- Networks and Telecommunications (A)
|
| Automatic |
- Automation and Industrial Computing (A)
|
Training places: FACULTY OF HYDROCARBONS AND CHEMISTRY (FHC) Fields of Training ST (Sthy)
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Science and Technology
(ST)
| Hydrocarbons
(National Recruitment
field)
|
- Mechanical Engineering :
- Transportation and Distribution of Hydrocarbons (A)
- Mechanic Oilfield (A)
- Mechanics of Petrochemical Units (A)
- - Petroleum Geophysics (A)
- Economy of Hydrocarbons (A)
- Petroleum Engineering :
- Hydrocarbons Production (A)
- Wells Drilling (A)
- Automation of Industrial Processes :
- Automatic Command (A)
- Electrical Engineering :
- Industrial Electricity (A)
- Process Engineering :
- Refining (A)
- Petrochemical Technology (A)
- Instrumentation in the Petrochemical Industry (A)
- Health Safety Environment (A)
|
Places of training: FACULTY OF ECONOMICS, BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES Fields of Training SECSG
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Economics, Management and Commercial Sciences
(SEGC)
| Commercial Sciences
|
- Finance and International Trade (A)
- Service Marketing (A)
- Hotel and Tourism Marketing (A)
|
| Management Sciences
|
- Management (A)
- Gestion Public (A)
- Financial Management (P)
|
| Economic sciences
|
- - Insurance Economics (A)
- Quantitative Economics (A)
- International Economy (A)
- Economics and Management of Companies(A)
|
| Financial Sciences and Accounting
|
- Accounting and Audit (A)
- Thorough Accounting and Taxation (A)
- Finance and Insurance (A)
- Finance and Banks (A)
|
Places of training: FACULTY OF LAW AND POLITICAL SCIENCE (FDSP) Fields of Training DSP
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Law and Political
Sciences
(LPS)
| Law
|
- Public Law (A)
- Private Law (A)
- Business Law (A)
|
| Political Sciences
|
- Local Administration (A)
- International Cooperation (A)
|
Places of training: FACULTY OF LETTERS AND LANGUAGES (FLL)
Fields of Training DSP LLA, LLE
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Arabic Language and Literature (ALL)
| Linguistics Studies
|
|
| Literary Studies
|
- Ancient Arabic Literature (A)
|
| Critical Studies
|
- Modern and Contemporary Criticism (A)
|
| Letters and Foreign Languages (FLLE)
| English Language
|
- Literature and Civilizations (A)
- Language Sciences (A)
|
| French Language
|
- Literature and Civilizations ( (A)
- Language Sciences (A)
- Didactics of Foreign Languages (A)
|
Places of training: INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING (IGEE)
Fields of Training ST
| Fields of Training | Sectors (Mentions) | Specialties |
|---|
| Sciences and Technologies
(ST)
| Automatics
|
|
| Electrotechnics
|
|
| Electronics
|
|
| Telecommunications
|
|
((A): Academic degree, (P): Professional degree
Formations en Post-Graduation
DIPLOMES PREPARES EN POST-GRADUATION
Doctorat 3 ème Cycle : accessible aux titulaires d'un diplôme de master
durée : 3 ans
DOCTORAT 3 ème CYCLE
Faculté des Sciences
-
Informatique, Chimie, Physique,Activité Physique et Sportive Educative, Entrainement Sportif,Sciences Biologiques, Sciences Agronomiques, Biotechnologie, Mathématiques.
Faculté de Technologie
-
Génie des Procédés, Génie Mécanique, Sciences et Génie des Matériaux, Génie de l’Environnement, Energie Renouvelables, Génie Civil, Electromécanique, Génie Biomédical, Energétique,Télécommunication.
Faculté des Hydrocarbures et de la Chimie
-
Hydrocarbures (Exploitation et Maintenance des Equipements Pétroliers et Matériaux, Génie Pétrolier et Gazier, Géophysique Pétrolière, Géosciences Pétrolières, Géophysique, Commande Automatique, Electricité Industrielle, Forage des Puits), Génie Electrique, Génie des Procédés, Industries Pétrochimiques.
Faculté des Sciences Economiques, Commerciales et Sciences de Gestion
-
Sciences Economiques, Sciences de Gestion, Sciences Commerciales,Sciences Financières et Comptabilité.
Faculté de Droit
-
Droit, Sciences Politiques,
Faculté des Lettres et des Langues
-
Etudes Linguistiques littéraires, Etudes Linguistiques, Etudes littéraires, Français, Anglais.
Institut de Génie Electrique et Electronique
-
Génie Electrique, Automatique, Electronique.
ECOLES DOCTORALES ET MAGISTERS
Faculté des Sciences
Ecoles Doctorales :
-
Systèmes Informatiques et Ingénierie des Logiciels.
-
Etablissement habilité : Université des Sciences et de la Technologie Houari Boumediene.
-
Etablissement partenaire : Université de Boumerdès.
Magisters :
-
Mathématiques, Sciences Chimiques.
Faculté des Sciences de l'Ingénieur
Ecoles Doctorales :
-
Mécanique et Ingénietrie des Systèmes
-
Etablissement habilité : Université de Boumerdès.
-
Etablissement partenaire : Ecole Nationale Supérieure Polytechnique, Université de Chlef et Université de Médéa.
-
Sciences et Ingénierie Matériaux et Environnement
-
Etablissement habilité : Université de Boumerdès.
-
Etablissement partenaire : Université de Tizi-Ouzou, Université de Laghouat, Ecole Normale Supérieure de Kouba et Unité de Développement des Technologies du Silicium.
-
Matériaux et Mécanique Productique
-
Etablissement habilité : Ecole Nationale Supérieure Polytechnique.
-
Etablissement partenaire : Ecole Militaire Polytechnique et Université de Boumerdès.
Magisters :
Génie Mécanique, Génie Mécanique et Productique, Energétique, Sciences et Génie des Matériaux, Maintenance Industrielle, gnie des Polymères, Génie Alimentaire, Génie Civil et Génie Manufacturier.
Faculté des Hydrocarbures et de la Chimie
Magisters :
Chimie Appliquée, Ressources Minéales et Energétiques, exploitation des Gisements Pétroliers, Géophysique, Génie mécanique, Génie Electrique, Génie Electrique Electrothecnique, Economie de l'Energie Sciences Economiques, Traitement de Signal, Génie Chimiques, Génie Pétrolier et Gazier et Génie Electrique/Automatique.
Faculté des Sciences Economiques, Commerciales et des Sciences de Gestion :
Magisters :
Sciences Economiques, Sciences de Gestion et Marketing.
Faculté de Droit :
Ecole doctorale :
-
Droit et Sciences Politiques
- Etablissement habilité : Université de Tizi-Ouzou.
- Etablissement partenaires : Université de Boumerdès et Université de Bejaia.
Institut de Génie Electrique et Electronique :
Magisters :
Génie Electrique, Electronique, Génie Electrique et Electronique.

 (3).jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
 (2).jpg)
 (2).jpg)
 (2).jpg)
.jpg)